Obesity - Symptoms,Causes,Risk factor,Prevention
Overview
Obesity could be a complicated disorder involving an excessive
quantity of body fat.
Obesity isn't just a cosmetic concern.
It will increase your risk of diseases and health issues, like
cardiovascular disease, diabetes and high blood pressure level.
Being extraordinarily obese means that you're particularly
possible to own health issues associated with your weight.
The good news is that even modest weight loss will improve or
check the health issues related to obesity.
Dietary changes, raise physical activity and behavior changes will
help you slim down.
Prescription medications and weight-loss surgery are extra choices
for treating obesity.
November 26 Anti-Obesity Day (AOD) is observed in various parts of
the world
Symptoms
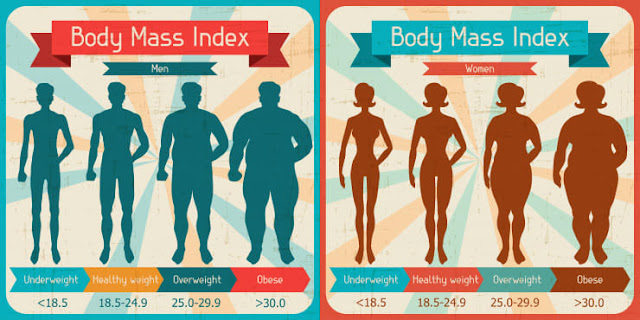
Obesity is diagnosed once your body mass index (BMI) is 30. or
higher.
Your body mass index is calculated by dividing your weight in
kilograms (kg) by your height in meters (m) square.
Below 18.5 Underweight
18.5-24.9 Normal
25.0-29.9 Overweight
30.0-34.9 Obese (Class
I)
35.0-39.9 Obese (Class
II)
40.0 and higher Extreme
obesity (Class III)
For most individuals, BMI provides an estimate of body fat.
However, BMI does not directly calculate body fat, therefore some
individuals, like muscular athletes, may have a BMI in the obese category even
though they don't have excess body fat.
Ask your doctor if your BMI is a problem.
When to see a Doctor
If you're thinking that you'll be weighty, and particularly if you
are involved regarding weight-related health issues, see your doctor or health
care supplier.
You and your supplier will judge your health risks and discuss
your weight-loss choices.
Causes
Although there are genetic, behavioral and hormonal secretion influences on weight, obesity occurs when you take in more calories than you burn through exercise and normal daily activities.
Your body stores these excess calories as fat.
Obesity will typically be derived to a medical cause, like
Prader-Willi syndrome, Cushing's syndrome, and other diseases and conditions.
However, these disorders are rare and, in general, the principal
causes of obesity are:
1. Inactivity.
If you are not extremely active, you don't burn as many calories.
With a sedentary lifestyle, you can easily take in more calories
every day than you use through exercise and normal daily activities.
2. Unhealthy diet and eating habits.
Weight gain is inevitable if you frequently eat additional
calories than you burn.
And most Americans' diets are too high in calories and are full of
junk food and high-calorie beverages.
Risk factors
Obesity most of the time results from a combination of causes and
contributory factors, including:
1. Genetics.
Your genes could effect the quantity of body fat you store, and
wherever that fat is distributed.
Genetics can also play a role in how expeditiously your body
converts food into energy and the way your body burns calories throughout
exercise.
2. Family lifestyle.
Obesity tends to run in families. If one or both of your parents
are obese, your risk of being obese is increased. That's not just because of
genetics.
Family members tend to share similar food and activity habits.
3. Inactivity.
If you are not terribly active, you don't burn as many calories. With a inactive life-style, you'll be able to simply absorb
additional calories on a daily basis than you burn through exercise and routine
daily activities.
Having medical issues, such as arthritis, can lead to decreased
activity, which contributes to weight gain.
4.Unhealthy diet.
A diet that is high in calories, lacking in fruits and vegetables,
full of fast food, and laden with high-calorie beverages and oversize portions
contributes to weight gain.
5.Medical problems.
In some individuals, obesity will be traced to a medical cause,
such as Prader-Willi syndrome, Cushing's syndrome and other conditions.
Medical issues, like inflammatory disease, also can lead to
decreased activity, which may result in weight gain.
6.Certain medications.
Some medications will result in weight gain if you do not
compensate through diet or activity.
These medications include some antidepressants, anti-seizure
medications, diabetes medications, antipsychotic medications, steroids and beta
blockers.
7. Social and economic issues.
Research has linked social and economic factors to obesity.
Avoiding fat is tough if you do not have safe areas to exercise.
Similarly, you'll not have been instructed healthy ways in which
of cooking., otherwise you might not have cash to shop for healthier foods.
In addition, the individuals you spend time with might influence
your weight — you are more probably to become fat if you have fat friends or
relatives.
8. Age
Obesity will occur at any age, even in young children.
But as you age, hormonal changes and a less active lifestyle
increase your risk of obesity.
In addition, the quantity of muscle in your body tends to decrease
with age.
This lower muscle mass results in a decrease in metabolism.
These changes additionally cut back calorie wants, and can make it
harder to keep off excess weight.
If you do not consciously manage what you eat and become a lot of
physically active as you age, you will likely gain weight.
9. Pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a woman's weight necessarily increases.
Some women's realize this weight tough to lose once the baby is
born.
This weight gain might contribute to the event of fatness in
girls.
10. Quitting smoking.
Quitting smoking is often associated with weight gain.
And for a few, it can lead to enough weight gain that the person
becomes obese.
In the long-term, however, quitting smoking is still a greater
benefit to your health than continuing to smoke.
11. Lack of sleep.
Not obtaining enough sleep or obtaining an excessive amount of
sleep will cause changes in hormones that increase your craving.
You may additionally crave foods high in calories and
carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain.
Even if you have got one or additional of those risk factors, it
doesn't mean that you're destined to become obese.
You can counteract most risk factors through diet, physical
activity and exercise, and behavior changes.
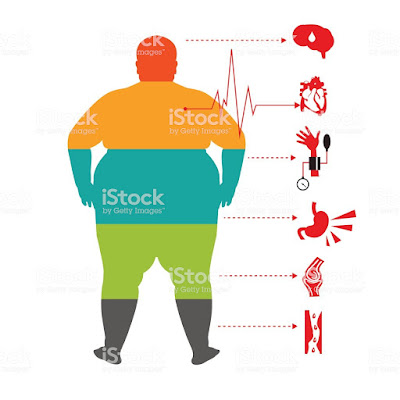
Complications
If you are obese, you are more likely to develop variety of doubtless serious health issues, including:
1. High triglycerides and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
2. Type 2 diabetes
3. High blood pressure
4. Metabolic syndrome — a combination of high blood sugar, high blood pressure, high triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol
5. Heart disease
6. Stroke
7. Cancer, including cancer of the uterus, cervix, endometrium, ovaries, breast, colon, rectum, esophagus, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidney and prostate
8. Breathing disorders, including sleep apnea, a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts
9. Gallbladder disease
10. Gynecological problems, such as infertility and irregular periods
11. Erectile dysfunction and sexual health issues
12. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a condition in which fat builds up in the liver and can cause inflammation or scarring
13. Osteoarthritis
Quality of life
When you're obese, your overall quality of life may be diminished. You may not be able to do things you used to do, such as participating in enjoyable activities. You may avoid public places. Obese people may even encounter discrimination.
Other weight-related problems which will have an effect on your quality of life include:
1. Depression
2. Disability
3. Sexual problems
4. Shame and guilt
5. Social isolation
6. Lower work achievement
Prevention
Whether you are in danger of changing into weighty, presently overweight or at a healthy weight, you'll take steps to stop unhealthy weight gain and connected health issues.
Not amazingly, the steps to prevent weight gain are the same as the steps to lose weight: daily exercise, a healthy diet, and a long-term commitment to watch what
you eat and drink.
1. Exercise regularly.
You need to urge 80 to 180 minutes of moderate-intensity activity every week to prevent weight gain.
Moderately intense physical activities embrace quick walking and swimming.
2. Follow a healthy eating plan.
Focus on low-calorie, nutrient-dense foods, like fruits, vegetables and whole grains.Avoid saturated fat and limit sweets and alcohol.
Eat 3 regular meals daily with restricted snacking.
You can still get pleasure from tiny amounts of high-fat, high-calorie foods as an infrequent treat.
Just make sure to decide on foods that promote a healthy weight and healthiness most of the time.
3. Know and avoid the food traps that cause you to eat. Identify situations that trigger out-of-control eating.
Try keeping a journal and write down what you eat, what proportion you eat, once you eat, however you feel and the way hungry you're.After a while, you should see patterns emerge.
You can set up ahead and develop methods for handling these kinds of situation and stay in control of your intake behaviors.
4. Monitor your weight regularly.
People who weigh themselves a minimum of once every week are a lot of productive to keep off excess pounds.Monitoring your weight will tell you whether or not your efforts are working and might help you notice little weight gains before they become huge issues.
5. Be consistent.
Sticking to your healthy-weight arrange throughout the week, on the weekends, and amidst vacation and holidays the maximum amount as attainable will increase your possibilities of long-run success.
To Remain healthy YOGA is one of the most important factor. Read more....


Comments
Post a Comment